Synology NAS Devices: Which One to Choose?
When there is no free space left in the chassis of your server to install hard disk drives, yet you still require more storage capacity, a good idea is to consider using NAS (network attached storage) devices. Moreover, NAS devices can be used not only for extending storage capacity, but also for backing up data, and as a media server for storing and playing multimedia content.
Synology is a leader in producing NAS devices and provides a wide range of NAS models. Selecting the proper NAS device can be a confusing and difficult task for new users faced with the choice of NAS for the first time. We will help you select NAS that can better fit your needs by reviewing the following devices:
- Synology DS216j
- Synology DS218+
- Synology DS418
- Synology DS918+
Also, we will cover the main Synology NAS features and capabilities, the common criteria for model classification, and how to use Synology NAS as a reliable and secure Backup Appliance with NAKIVO Backup & Replication.
General Synology NAS Features and Capabilities
Before choosing one or another model of Synology NAS you should answer the following questions:
- How are you going to use NAS?
- How much storage space do you need? Do you need redundancy? Do you want to use RAID?
- What features do you need? Do you need video transcoding, installing additional applications etc.?
- What CPU and memory configuration is required? (This is dependent on used features).
Let’s explain features and capabilities that are available for Synology NAS devices as well as possible use cases.
Use cases
The first and most prevalent use case of NAS is storing data that must be accessible via network. NAS can be used as a file server to allow users to edit files and store them on a NAS device which is most optimal for small organizations. Home users can store photo, video, audio and other types of media content on NAS and access that content from different devices connected to the home network. Synology NAS can be used to store backups as well as for creating a dedicated backup appliance.
Storage
Synology NAS devices are produced without disk drives. This is not a disadvantage – you can buy any needed hard disk drives (HDD) or solid state drives (SSD) with the necessary characteristics and install them into your Synology NAS device; consider it as freedom of choice. Vendors that sell NAS devices with preinstalled disks usually have an artificial, contrived limit on the list of disk models that can be installed on NAS. At present, the maximum capacity of hard disks you can install into Synology NAS devices is 16 TB. Before choosing a NAS model, you should plan the maximum storage capacity you need used on NAS, whether to use RAID or not, and the maximum number of disks that can be installed into the NAS device, as well as the possibility of a disk hot swap. All these parameters should be considered together.
Note: Check on the official web site of Synology to verify the maximum supported size of a disk for the NAS model you want to buy. Be aware that the limit for a single volume size for 32-bit processors is 16 TB and for 64-bit processors is 108 TB for Synology NAS models. Some NAS models support the 200-TB maximum size for a volume. Sometimes the maximum volume size can be increased from 108 TB to 200 TB after upgrading memory to 32 GB.
Note: It is recommended that you use all disks with the 4-KB sector size (Advanced format) or all disks with the 512-B sector size in the same array.
Number of bays
Bays are slots that are present in a chassis of a NAS device and are intended to have disks installed into them. There is no reason to buy NAS with less than two bays for disks. Synology provides NAS devices with 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 12, 16, and 24 bays for disks. Notice that some models have bays compatible with 3.5″ disks and 2.5″ disks, though there are certain Synology models that have bays only for 2.5″ disks.
Hot swap
Some NAS models have a construction that requires you to remove the screws that hold a disk in the bay, yet there are other Synology NAS models that support hot swap of disks. You can eject one disk and insert another quickly without powering off a NAS device and spending the time needed to disassemble a chassis as well as removing the screws required to uninstall a disk from NAS. The hot swap feature can be useful when you use RAID in the configuration of your NAS.
RAID
The most of Synology NAS models support the RAID option (Redundant Array of Independent Disks). Let’s consider RAID types and implementations supported by Synology NAS devices.
Traditional RAID types
RAID 0 is a form of disk striping that provides no redundancy. If you add two disks into this array type, the capacity of disks is added to the total. For example, if your RAID 0 consists of two 1-TB disks, the available capacity to store files is 2 TB. When data is written to disks of RAID 0, block1 is written to disk1, block2 is written to disk2, block3 is written to disk1, block4 is written to disk2, etc. Reading and writing speed is increased by about two times, but there is no fault tolerance for RAID 0 (fault tolerance is 0 and is equal to the RAID number). If any disk of the array becomes corrupted, you lose data. At least two disks are needed to create RAID 0.
RAID 1 is a kind of disk mirroring that provides 100% redundancy (1=100% that is equal to the RAID number). If two disks are added into the array, the available capacity remains the same. For example, if your RAID 1 consists of two 1-TB disks, the available disk space to store files is 1 TB. When data is written to disks of RAID 1, block1 is written to disk1 and is duplicated to disk2, block2 is written to disk1 and is duplicated to disk2, etc. RAID 1 has the highest level of fault tolerance and is recommended for storing important data. The writing performance is slower for RAID 1 but if one of the disks becomes corrupted, all data is available on the second disk, and you can replace the corrupted disk, rebuild the array, and after rebuilding, continue using RAID 1. Two disks are needed to create RAID 1. It is recommended that you use disks of the identical capacity for more efficient disk usage.
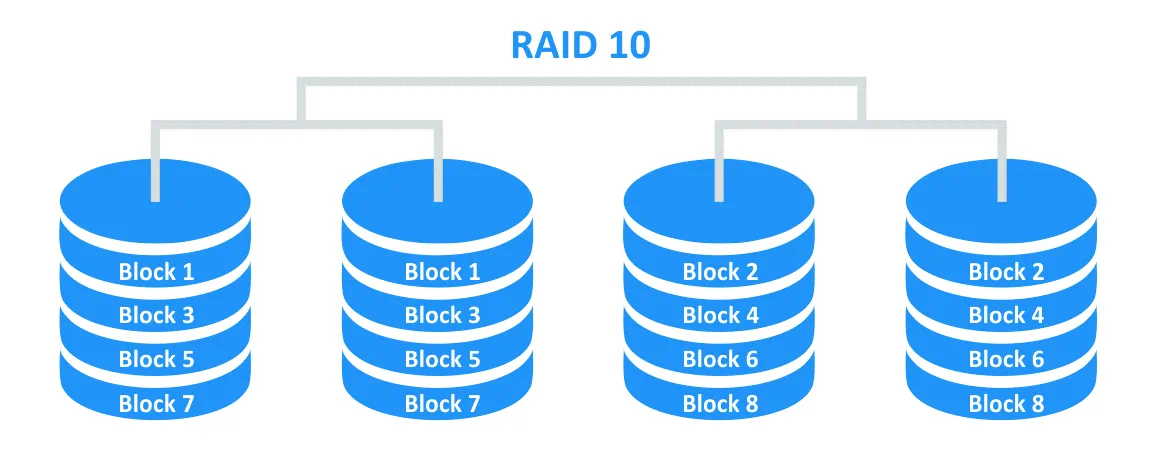
RAID 10 is a combination of RAID 1 and RAID 0 (RAID 1+0). Disks are mirrored and then they are striped. Four disks are required for creating RAID 10. RAID 10 can survive after the failure of any one disk and can survive after the failure of two disks which belong to different mirrors. If you create RAID 10 by using four 1-TB disks, the available capacity for storing data is 2 TB, which is 50%. RAID 10 provides reliability that is sufficiently high and allows you to achieve high capacity of the array. The balance of fault tolerance and performance is the primary benefit of RAID 10.
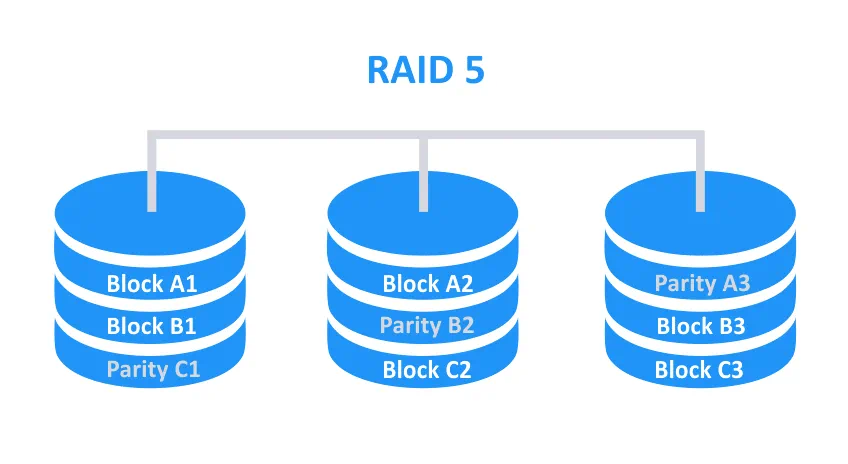
RAID 5 is another RAID type that requires at least three disks. Capacity equal to the capacity of one disk drive is used for redundancy, and redundant data is distributed across all disks of RAID 5. The available disk space for storing data is the summed capacity of all disks minus capacity of one disk. It can be described with the formula: RAID5 capacity = (n-1)*hddsize where n is the number of disks. For example, if you use three 1-TB disks in RAID 5, you get 2 TB of useable disk space. Theoretically RAID 5 can survive the failure of one disk. However, using RAID 5 is not always an optimal choice, especially for production environments.
This is primarily because RAID 5 was invented in 1987 when capacity of disks was low (about 21 MB) and disk revolutions per minute (RPM) was 3600. Nowadays, the capacity of a basic disk can start from 1 TB and disk plates are rotated with a speed of 5400 and 7200 RPM. The maximum available disk capacity in 2019 is 12 TB. Disk speed is provided not only by plates’ rotation speed which has been increased twice its earlier level, but also depends on recording density, cache, firmware and interface. However, hard disk capacity has increased much more than disk speed since the time of RAID 5’s invention. When one disk of RAID 5 is damaged and you replace the damaged disk with a healthy disk, the RAID 5 rebuilding process begins. The rebuilding process for RAID 5 is extremely time-consuming and takes a long time for modern disks since their speed is not high compared to their disproportionately large capacity. During the array rebuilding, a RAID controller must read all remaining redundant data from all disks and write that data to a new disk that was exchanged. During rebuilding, RAID 5 has no redundancy and is extremely vulnerable.
The Bit Error Ratio (BER) is the parameter of disks evaluated by a manufacturer that shows the probability of read operation failure. The BER value for desktop disks is usually equal to 10^14 and modern disks of top series have a BER value of 10^15. This means that a disk manufacturer guarantees the probability of read failure not worse than 1 failed bit per 10^14 read bits. 10^14 bit is equal to approximately 11 TB, hence after reading 11 TB of data from a disk (since you began using the disk) the probability of failure when reading a bit increases to 100%. If a bit cannot be read, then a 512-byte block cannot be read (if a hard disk supports 4-KB blocks (Advanced Format), a block size can be 4096 bytes). If a block cannot be read to recover data of RAID 5, the rebuilding process will fail. Now you can imagine the amount of time needed to rebuild RAID 5 and calculate the probability of failure that increases with the increased capacity of disks used in RAID 5.
Note: The disk capacity is measured in Bytes (B), Kilobytes, Megabytes (MB), Gigabytes (GB), Terabytes (TB), etc. Unfortunately, capacity of modern disks is specified not in the binary system where 1 MB = 1024 KB, but in a decimal system where 1 MB = 1000 KB.
RAID 6 is the modified version of RAID 5 where redundant data for recovery is stored on two disks instead of one, and is distributed across all disks of the array. Hence, there is two disk redundancy in RAID 6. Four or more disk drives are required to create RAID 6. RAID 6 can survive if one disk fails and twice the level of redundant data in RAID 5 which can protect against read failures during rebuilding. Write speed for RAID 6 is less than for RAID 5.
Specific RAID options available on Synology NAS
Basic. This mode should be selected when you would like to use one disk without RAID. This mode is similar to using a hard disk on a laptop when you have no RAID options.
JBOD (just a bunch of disks) is a non-RAID mode that allows you to combine multiple disks of different capacity into a big single volume. The capacity of the JBOD volume is the sum of sizes of all disks included to JBOD. There is no redundancy and fault tolerance because JBOD is not RAID. You can use an odd number of disks and disks of different capacity, unlike RAID 0.
SHR (Synology Hybrid RAID) is a specific proprietary mode that can be used for odd number of disks of different capacity. Disk capacity is divided into lower chunks that are grouped to an array automatically. One or two disk redundancy can be enabled for SHR. SHR allows you to exchange the smallest disk to a larger disk and gradually increase capacity of the SHR volume. One more advantage of using SHR is the ability to migrate to Synology NAS devices that have more disk bays with saving SHR configuration. For example, you can migrate from your 2-bay Synology NAS to a 5-bay Synology NAS and so on by migrating disks.
RAID implementations
There are three main implementations of RAID: Hardware RAID, software RAID and fake RAID.
Hardware RAID is the most reliable RAID implementation based on a physical RAID controller. A separate RAID card is connected to a motherboard. Disk drives are connected to ports of the RAID controller. Hardware RAID is OS-independent and doesn’t load the CPU for parity calculations and related tasks. Hardware RAID can be used on machines with different operating systems and it is recommended that you install RAID controller drivers to unlock some features, for example, checking S.M.A.R.T. of disks connected to the RAID controller. The most reliable hardware RAID can be built by using a RAID controller that has cache and a battery to avoid errors. This is a recommended solution for the enterprise level.
Software RAID is the RAID implementation on the OS (operating system) level that is usually based on the modified driver (that emulates work of a RAID controllers). A physical RAID controller is not used in this case. Software RAID solutions such as mdadm (mdraid), are available in Linux distributions. Software RAID cannot be implemented on all operating system and some solutions may cause errors. The CPU and RAM of a physical computer are utilized to calculate operations of software RAID. Software RAID is affordable for home and corporate users.
Fake RAID is an optional built-in feature of a chipset on a motherboard that works in combination with a special operating system driver that is usually provided for Windows systems. Fake RAID cannot be used on Linux systems – Linux will not boot from fake RAID and will recognize disks as independent disks. Hence, if you are not sure whether your RAID is hardware RAID or fake RAID, boot Linux from the live DVD. This allows you to check the possibility of direct managing disks from an operating system that bypasses a RAID controller. Fake RAID works primarily as software RAID while redirecting some instructions to the chipset of the mainboard instead of the CPU, and is overall the most unreliable implementation of RAID. Nevertheless, the CPU is the main calculation unit for operation of fake RAID.
The majority of NAS devices provide software RAID. Linux md RAID is used as software RAID on the majority of Synology NAS devices. Using software RAID implementation on Synology NAS devices allows you to mount disks to the Linux computer manually and recover data if needed.
Available RAID options depend on the model of Synology NAS, for example, a model of NAS with two disk bays doesn’t support RAID 10, RAID 5 and RAID 6.
Disk models
Keep in mind which disks you would like to use in your NAS because this decision may have an impact on which model of Synology NAS you select. Physically, you can install any SAS and SATA disks into NAS with SAS ports, but you can only install SATA disks into a NAS device with SATA ports. The 2.5″ disks can be installed in 3.5″ bays but the inverse is not possible. Keeping in mind these features, you can install any supported disk into your Synology NAS. However, there are HDD models that are positioned by vendors as disks optimized to work in NAS. Such disks have firmware that prevents disk heads from parking when there are no requests to read/write data from a disk, in addition to preventing disk plates from stopping and other features for operating in the 24×7 mode (unlike starter disks of the desktop class). Hard disks of the NAS series are constructed to minimize heating and vibration because their aim is to be used in a small NAS box, not in a spatial chassis of desktops or servers where powerful cooling systems can be installed. The NAS series of disks are quiet, so as to provide no disadvantages to home users. Examples of hard disk series that are positioned as NAS series are Western Digital Red (5400 RPM), Seagate IronWolf and Western Digital Red Pro (7200 RPM), and Seagate IronWolf Pro (7200 RPM).
Unlike desktop disks, NAS-oriented disks support SCT ERC (S.M.A.R.T. Command Transport Error Recovery Control) that is known as WD TLER (Time Limited Error Recovery) for disks produced by Western Digital and allows you to set the timeout for error correction. This feature prevents RAID degrading if a block cannot be read from a disk that belongs to RAID. If a block cannot be read/written for a specified time, for example 7 seconds, control is transferred from a disk to a RAID controller (if a RAID controller is present).
Keep in mind that if your NAS model has one 1-Gigabit network interface, installing the fastest disk drives whose data transfer speed is more than 1 Gigabit per second (125 MB/sec) may be not rational since the network interface will result in a bottleneck.
Synology NAS features
Synology NAS devices support a lot of interesting features. Let’s consider some of them.
Video transcoding is an option that allows you to encode (convert) video and audio stored as files on NAS. This enables multimedia devices such as Smart TV and applications such as media players to play video and audio content that was unsupported before transcoding. You get new output files after transcoding source files. CPU performance and sufficient memory capacity is required to use this feature. Video resolution can also be changed during transcoding. Synology NAS video transcoding is a feature that may be most attractive for home users. If your NAS doesn’t support video transcoding, don’t despair, as you can still encode (convert) video to the necessary formats on your personal computer manually and copy files over the network to NAS.
Plex video streaming can be enabled on the appropriate models of Synology NAS. To install the Plex Media Server, the Plex Server application (package) must be installed on Synology NAS in the Package Center that is available in the web interface of the NAS device. After installing the Plex Server, you can stream your videos stored on NAS and watch those videos on devices such as computers, smartphones, tablets, Apple TV, etc.
Availability for installing applications. The more powerful hardware that is installed on a NAS device, the more applications are supported by this NAS device; the Plex Media Server is just one of these examples. Moreover, you can install the data protection software on your Synology NAS and back up data to the NAS via the network.
Supported file sharing protocols. The more file sharing protocols are supported by your Synology NAS, the more universal your NAS device is. As you know, NFS is a native protocol for sharing files in Linux, SMB in Windows, and AFP in macOS. You can install additional third party applications (clients) on aforementioned operating systems, for example, to make Windows able to access the NFS share or enable macOS to access the SMB share. Another solution is to share a directory on your NAS by using SMB, NFS, and AFP protocols at once to allow an operating system using native file sharing clients to access shared files over the network. The following sharing protocols can be supported by diverse models of Synology NAS devices:
- SMB (Server Message Block)
- NFS (Network File System)
- AFP (Apple Filing Protocol)
- FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
- WebDAV (Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning) is the protocol for data transferring that operates over HTTP 1.1.
- iSCSI (Internet Small Computer Systems Interface) is a block-level sharing protocol that is different from the protocols mentioned above. iSCSI is used to connect shared storage to VMware ESXi hosts in VMware vSphere environments (including VMware clusters) and can be used to connect an iSCSI target as a storage device to a VirtualBox VM.
Before buying a NAS device, check its specification and make sure that all sharing protocols you need are supported.
Hardware configuration
Hardware configuration of Synology NAS devices varies depending on the model and supported features.
CPU. The CPU architecture can be x86-64, ARM64, ARM. Intel processors that have the x86-64 architecture are used for more advanced configurations, while ARM processors (by Marwell, Realtek and other vendors) are mainly used for basic configurations. The wide list of Intel processors families including Atom, Celeron, Pentium, and Xeon is used by Synology for NAS devices.
Memory. A more powerful configuration has more memory. Some Synology NAS devices provide an option for upgrading memory – you can buy a RAM module and insert it into an empty DIMM (SODIMM) slot. The newer DDR4 memory standard works on a higher frequency than the DDR3 standard and provides better performance. The possibility of memory upgrade is not available for all Synology NAS models.
The possibility to connect an expansion unit. Some Synology NAS devices allow you to connect an expansion unit which is a device that has additional disk bays. The expansion unit can be connected to the main Synology NAS device via eSATA interface. Some models of Synology NAS have two eSATA ports to connect expansion units. For example, the RX1217sas expansion unit can be connected to the following Synology NAS models: FS6400, FS3400, FS3017, FS2017, SA3400, RS18017xs+.
The possibility of using expansion units offers you greater scalability. When all bays of your NAS contain hard disks of the maximum possible capacity (16 TB at this time) and you cannot change the disks to those having higher capacity, you can buy an expansion unit and install new hard disks into the expansion unit.
Ports and interfaces
Synology NAS devices can be equipped with the following ports/interfaces.
SAS (Serial Attached SCSI) is an enterprise level internal disk interface that can be used to connect SAS and SATA disks. SAS supports an SCSI command set for transferring data and provides more performance, expandability, scalability, and high reliability, which are the advantages of the SAS interface. SAS was provided as the result of evolution of SCSI and is recommended for datacenters and production environments.
SATA (Serial ATA) is a modern substitution of the IDE interface. Only disks with SATA interface can be connected to SAS ports. SATA disks are affordable and can be used by both corporate and home users.
eSATA (External Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) is used to connect external hard disk drives. Unlike USB, eSATA is a native interface for connecting disks and data transferring. eSATA is primarily used to connect external disks (disks must be connected to a power supply separately). In case you are deploying Synology NAS devices, eSATA can be used to connect Synology expansion units, allowing you to connect more disks to your NAS and providing better scalability. Some Synology NAS models can have more than one eSATA port.
USB 2.0 (Universal Serial Bus) can be used to connect different devices. If your Synology NAS has USB 3.0 ports that provide higher speed, connecting external USB 3.0 hard disks to USB 2.0 ports is not a rational option. USB 2.0 can be used to connect a printer to Synology NAS and configure a NAS device as a print server. USB 2.0’s speed is more than adequate for printers.
USB 3.0 is a high speed interface. In case you are using Synology NAS, you can connect external USB 3.0 hard disk drives to your NAS and copy data from a USB HDD to NAS and vice versa.
RJ-45 (Ethernet 1-Gigabit) is the interface for network connections, as at least one Ethernet port is present on NAS devices. There are Synology NAS models that have more than one Ethernet port. Multiple Ethernet ports can be used to configure link aggregation (NIC teaming) and increase bandwidth when more than one host is connected to NAS simultaneously. Some Synology NAS models of the top class have 10-Gbit Ethernet RJ-45 ports.
COM port provided on some NAS devices can be used for management and service operations.
Model Classification
At the first glance, the naming of Synology models may seem rather confusing. However, the naming system of Synology is actually quite rational and convenient. What is the difference, you may ask, between Synology RT2600AC, Synology DS216j, Synology DS1618+, and Synology FS2017? First of all, Synology RT2600AC is not NAS, it is a Wi-Fi router. Three other devices are NAS devices, though, that were produced in different years and have a different number of disk bays. If you are familiar with the naming principle, you can understand some differences between Synology NAS models after looking at NAS names. The template of naming Synology NAS models is as follows:
LL NNNN EE
Where:
LL are the leading letters
NNNN or NNN is the number (middle) part
EE(E) are the ending characters
Let’s consider each part in detail.
Leading letters
DS – DiskStation. The desktop design. These series can be used for both home and corporate users. The examples of DS series are DS2819+, DS218Play, DS118, DS416slim, etc.
DX – DiskStation Expansion unit for DiskStation Synology NAS models. The examples of DX models are DX513, DX1215, etc.
RS – RackStation. The rackmount design oriented for corporate usage. Synology NAS models of the RS series are RS217, RS819, RS2818RP+, etc.
RX – RackStation Expansion unit with rackmount design. Examples of RackStation expansion units are RX418, RX1216sas, RX1217, etc.
FS – FlashStation. The desktop design series for high-performance 2.5″ disks aimed for enterprise and business users. NAS devices of the FS series are produced in desktop and rackmount design. The majority of Synology NAS models of the FS series run on Intel Xeon processors. FS1018, FS2017, FS6400 are examples of the FS series models.
NVR – Network Video Recorder. The server design, intended to work as a video recorder. IP cameras can be connected to Synology NAS models of the NVR series to record video. NVR216 and NVR1218 are members of the NVR series.
VS – VisualStation. Synology NAS models of these series are intended to work as a surveillance server by connecting IP cameras and recording video from cameras to disks installed on NAS. A convenient web interface is provided to monitor connected cameras.
SA series represents the top series of Synology NAS models together with FS and XS series. SAS interface is provided, an example of which Synology SA3400.
Number (middle) part
This part contains three or four digits. The first one or two digits signify the maximum supported number of bays for disks (separately or with an expansion unit). For example, Synology DS718+ contains only two bays, but the DX517 expansion unit that contains 5 bays can be connected to DS718+ to increase the total number of bays to 7. Synology DS217 has only two bays and doesn’t support connecting to an expansion unit. See the detailed specification of the appropriate Synology NAS model to better understand how much bays are available in one or another NAS model without an expansion unit.
The second two digits indicate the Synology NAS release year. For example, Synology DS217 was manufactured in 2017 and Synology DS718+ was manufactured in 2018.
Ending characters
This part consists of one character, letters, or a word:
SE – the entry level series (single-role edition) that contains the lowest hardware specification, provides only basic features and can meet only basic needs. The most affordable price is for devices of the SE series. Examples: DS216SE.
J – The low price models that are affordable for most users. The price is about 20% higher than for the SE series. Examples: DS218j, DS418j.
Slim – software and hardware capabilities are the same as for the J series, but they are meant to use SSD disks. Examples: DS416slim, DS419slim, DS620slim.
Value series (Standard series) are intended for the intermediate level. The standard series refers to the series without characters after the number (middle) part. Examples: DS118, DS218, RS819, NVR216, FS3017.
Play – the series is positioned as a series for home usage and is optimized for storing and playing multimedia content such as photos, videos, music, etc. The models of this value series usually support video transcoding and don’t contain any characters after the number (middle) part of the model name. Examples: DS416play, DS418play.
+ (Plus) – the high-end series that run on the top hardware, provide the top features, and can be used for personal and business purposes. The majority of features available for the Play series and other lower series are available. Video transcoding is not available on all Synology NAS models of the Plus series. Examples: DS713+, DS918+, RS815+, RS818+, DS1515+.
XS – the top class series that is positioned as the best series. The price for Synology NAS models of XS series is high, performance is the best, and extended warranty and support are provided. Examples: RC18015XS, DS3617XS, RS1619XS.
SAS – SAS interface for connecting disks is provided. Examples: RX1216sas, RX1217sas.
RP – redundant power supply can be connected. Synology NAS models of the RP series have two (slots) for connecting an external power supply or two power supplies (actual for Rackmount design). The second power supply can be bought separately and is not always included with the kit. Examples of the RP series: RS815RP+, RS2416RP+.
Now after familiarizing yourself with possible characteristics and model classification, we can go to the Synology NAS review on example of four popular devices and compare Synology NAS models.
Synology DS216j Review
Synology DS216j is the most affordable model of the DS216 line of Synology models that is designed as a white box of the desktop form-factor. The external parts of the box are made of plastic and internal parts are metal. This NAS model has convenient software and can be used as a media player. The cooling system is effective and quiet.
Audio transcoding to MP3 is supported to reduce streaming bandwidth. Software used on Synology DS216j is optimized to transfer large files, generate proto preview (thumbnails), and browse photos. However, Synology DS216j is not designed for video transcoding. If video transcoding is a crucial feature for you, consider buying Synology DS216play or other models. By using Cloud Station, users can synchronize their files with local computers, other Synology NAS devices and public cloud storage such as Amazon S3, Microsoft Azure etc.
Two 3.5″ or 2.5″ HDDs and SSDs can be installed. The maximum supported capacity of disks is 8 TB. Hence, the maximum storage size you can have with Synology DS216j is 16 TB (2 x 8 TB). You can use RAID options to create one 16-TB volume. Hot swap of disks is not supported because there are no drive trails. As a result, you should disassemble the NAS box and remove the screws to unmount disks from the bay. The eSATA port is missing. BTRFS (file system) is not supported.
Synology DS216j is a good device for users who need NAS for basic tasks and an affordable price tag. Data transfer speed is reasonably high for a device of the beginner class.
Specification:
Number of Bays: 2 (3.5″)
Expansion unit support: No
Disk interface: SATA 3
Maximum disk capacity: 2 x 8 TB
Hot swap of disks: No
External ports: 2 x USB 3.0, 1 x 1-Gbit Ethernet (RJ-45)
Processor (CPU): Marvell Armada 385 88F6820 (1.0 GHz, dual-core, ARM 32-bit)
Memory (RAM): 512 MB DDR3
Sharing Protocols: iSCSI, SMB (CIFS), AFP, NFS, FTP, WebDAV
RAID modes: Basic, JBOD, SHR, RAID 0, RAID 1
Features: NAKIVO Backup & Replication cannot be installed on this NAS; audio transcoding to MP3
Dimensions: Height 165 mm, Width 100 mm, Depth 225 mm
Synology DS218+ Review
Synology DS218+ is another budget model of NAS, though it provides a greater set of interesting features than Synology DS216j. Regarding the design, Synology DS218 is designed as a black box with 4 LED indicators on the front panel (Status, LAN, Disk1, Disk2), one USB 3.0 port on the front panel, and external ports (two USB 3.0 ports, one eSATA port, one RJ-45 Gigabit Ethernet port, power port, and Kensington Security slot) on the back panel. There are two bays for disks that can be connected via SATA interface. The maximum supported capacity of disks is 14 TB. Hence, the maximum storage space you can provide with Synology DS218+ is 28 TB (2 x 14 TB). The Btrfs file system is supported and you can utilize all of its advantages. Drive trails are present, and can be accessed after opening the front panel. Hot swap is enabled. A 92-mm fan provides good ventilation for hard disk drives and other internal parts.
This NAS model features a dual-core Intel Celeron processor and 2 GB of RAM. The amount of RAM can be increased up to 6 GB in order to perform operations that need high performance due to a free DDR3 slot. Synology DS218+ supports real-time 4K video transcoding. You can also install a lot of supported application packages such as email server, web server, media streaming server, data backup server, surveillance station etc. The Quick Connect feature allows you to access files on NAS from the internet without configuring port forwarding on your router.
Synology DS218+ is a good solution for SOHO (small office – home office) users and for home users who need relatively high performance and extensive multimedia features. This NAS is a good combination of price and quality values.
Specification:
Number of bays: 2
Expansion unit support: No
Disk interface: SATA 3
Maximum disk capacity: 14 TB
Hot swap of disks: Yes
External ports: 3 x USB3.0, 1 x eSATA, 1 x 1-Gbit Ethernet (RJ-45), Kensington Security slot
Processor (CPU): Intel Celeron J-3355 (2,5 GHz, 64-bit, 2 cores)
Memory (RAM): 2 GB DDR3 (6 GB is the maximum supported limit)
Sharing Protocols: iSCSI, SMB (CIFS), AFP, NFS, FTP, WebDAV
RAID modes: RAID 0, RAID 1, Basic, JBOD, Synology Hybrid RAID
Features: NAKIVO Backup & Replication can be installed; video transcoding, surveillance station (max 25 cameras, 2 free licenses included) etc.
Dimensions: Height 165 mm x Width 108 mm x Depth 232 mm
Synology DS418 Review
Synology DS418 is an affordable four-bay NAS model that can satisfy home and office users by providing a universal modular platform to store files, back up data, share data with users over the network, record videos from IP cameras, etc. Synology DS418 was designed as a black box of the desktop form factor with vertical disk bays that are numbered. The design of disk trays is hot swappable for 3.5″ disks, and 2.5″ disks must be screwed in. The maximum disk drive capacity supported by Synology DS418 is 16 TB and maximum total storage capacity can be 64 TB (4 x 16 TB). Internal disks can be formatted in Btrfs or Ext4 file systems and external disks with Btrfs, Ext3, Ext4, NTFS, FAT32, HFS+ and exFAT* file systems are supported.
Synology DS418 has a 64-bit quad-core ARM processor (Realtek RTD1296) whose frequency is 1.4 GHz and 2 GB of DDR4 RAM. The processor performance is adequate for 10-bit 4K on the fly video transcoding. These are the following external interface ports on Synology DS418: two USB 3.0 ports (one on the front panel and one on the rear panel), and two RJ-45 (1-Gbit Ethernet) network ports. The active cooling system contains two 92-mm fans that can be configured to operate in three modes: Full-speed, Cool, and Quiet. The fans can be easily removed for cleaning them from the dust.
Four disk indicators, the status indicator and the power indicator are located on the front panel. LED indicators are adjustable, allowing you to reduce the level of emitted light when you want to sleep or if you find that LED indicators to be too bright for your eyes. Wake on LAN is available and allows you to save energy and power on NAS by using LAN when needed.
Specification:
Number of bays: 4
Expansion unit support: No
Disk interface: SATA 3
Maximum disk capacity: 16 TB
Hot swap of disks: Yes
External ports: 2 x USB 3.0, 2 x RJ-45 (1-Gbit Ethernet), Kensington Security Slot
Processor (CPU): Realtek RTD1296 (ARM 64-bit, 1.4 GHz, 4 cores)
Memory (RAM): 2 GB DDR4
Sharing Protocols: iSCSI, SMB (CIFS), AFP, NFS, FTP, WebDAV
RAID modes: RAID 0, RAID 1, DAID 10, RAID 5, RAID 6, Basic, JBOD, Synology Hybrid RAID
Features: NAKIVO Backup & Replication can be installed; video transcoding (10-bit, 4K, 60 FPS), surveillance station (2 free licenses, max. 30 cameras supported), Wake On LAN etc.
Dimensions: Height 166 mm x Width 199 mm x Depth 223 mm
Synology DS918+ Review
Synology DS918+ is another four-bay NAS model that provides greater scalability and is aimed at the small/medium size business market and home users. The external design of this Synology NAS model is similar to the design of Synology DS418 considered above. Synology DS918+ is a more advanced model and has a quad-core 64-bit Intel Celeron J3455 processor (1.5 GHz, 2.3 GHz boost frequency) with one 4-GB preinstalled DDR3 memory module. There is a second empty slot that allows you to upgrade RAM up to 8 GB (two 4-GB modules in total). The maximum disk size supported by Synology DS918+ is 16 TB. The maximum overall storage capacity is 64 TB (4 x 16 TB). If your business grows or the size of your digital home library increases, you can connect a 5-bay expansion unit and expand the total storage size up to 144 TB (64 TB + 5 x 16TB). You can connect a DX517 expansion unit to DS918+. Hot swap is available for 3.5″ and 2.5″ disks (2.5″ disks must be screwed into disk trays). The maximum single volume size is 108 TB.
Regarding internal ports, in addition to SATA ports, there are two M.2 (NVMe) drive slots that can be used to connect two SSD disks and use these disks as a high-speed cache. External ports are represented by two RJ-45 ports, two USB 3.0 ports (one on the front panel and another on the rear panel), and one eSATA port. Adjustable brightness of LED indicators on the front panel is supported. The cooling system consists of two 92-mm fans that can work in three modes: full-speed, cool, quiet. Video transcoding for 4K video is supported with the maximum of 30 FPS (frames per second). Synology DS918+ can be used as a surveillance station and supports up to 40 connected IP cameras. Two free licenses for IP cameras are included and if you wish to use more cameras, additional licenses are needed. The list of supported file systems for Synology DS918+ is the same as for Synology DS418.
Specification:
Number of bays: 4
Expansion unit support: Yes (a 5-bay unit)
Disk interface: 4x SATA3, 2 x NVMe
Maximum disk capacity: 16 TB
Hot swap of disks: Yes
External ports: 2 x USB 3.0, 2 x RJ-45 (Gigabit Ethernet), Kensington Security Slot
Processor (CPU): x64 Intel Celeron J3455 (4 cores, 1.5 GHz, 2.3 GHz burst)
Memory (RAM): 4 GB DDR3L (upgrade up to 8 GB is available)
Sharing Protocols: iSCSI, SMB (CIFS), AFP, NFS, FTP, WebDAV
RAID modes: RAID 0, RAID 1, DAID 10, RAID 5, RAID 6, Basic, JBOD, Synology Hybrid RAID
Features: NAKIVO Backup & Replication can be installed, video transcoding (4K, 30 FPS), surveillance station (max. 40 IP cameras, two free licenses included) etc.
Dimensions: Height 166 mm x Width 199 mm x Depth 223 mm
Using Synology NAS as a Backup Appliance
You have probably noticed that in each specification section, in the features list, there is a description whether NAKIVO Backup & Replication can be installed on one or another NAS. All Synology NAS models considered in this review except for Synology DS216j can be used to create a backup appliance.
NAKIVO Backup & Replication is a universal data protection solution that can be installed on Linux machines, Windows machines, and NAS devices to back up VMware virtual machines (VMs), Hyper-V VMs, Amazon EC2 instances, physical Linux machines and Windows servers. The full list of supported NAS devices is available to you in the NAKIVO helpcenter.
You can install NAKIVO Backup & Replication on your Synology NAS in the Package Center from the web interface of NAS. If NAKIVO Backup & Replication (full solution) is installed on another machine or device, you can install the NAKIVO Transporter only.